Key Takeaways
• A Bitcoin block is a data structure containing verified transactions, added to the blockchain through mining.
• It holds data like timestamps, a block subsidy (currently 3.125 BTC), and links to the previous block.
• Blocks keep the Bitcoin ledger secure, decentralized, and functional.
Have you ever wondered how Bitcoin transactions work?
The answer lies in the structure of the blockchain. More specifically, something called a Bitcoin block.
At the core of the Bitcoin network is a decentralized system that relies on these blocks to function efficiently and securely. Understanding what a Bitcoin block is can provide better insight into how the entire blockchain operates.
What is a Block in Bitcoin?
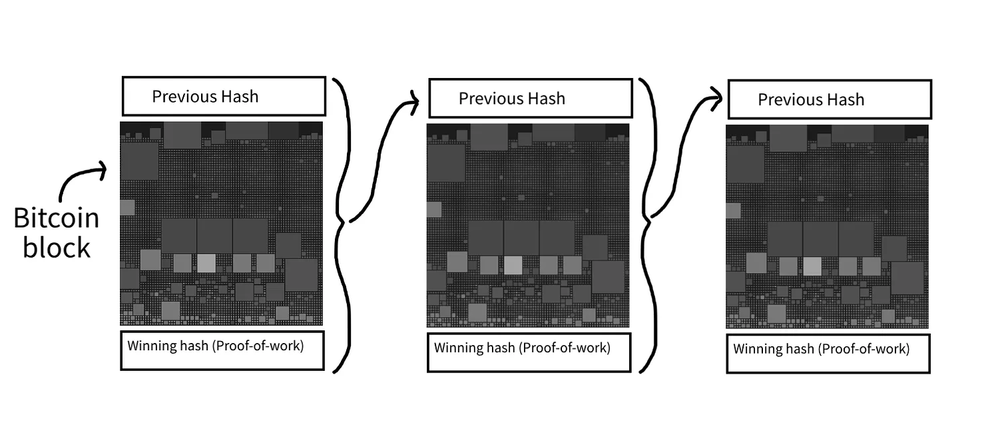
A Bitcoin block is a container of recent Bitcoin transactions.
These transactions are grouped together by a node, verified, and then added to a memory pool. Each block in the blockchain holds essential data that is important to the transaction, such as:
- Timestamp: Records the exact time the block was mined. This essentially provides a history of the blockchain. It’s used to calculate mining difficulty adjustments based on block production time.
- Hash of the Previous Block: Creates a cryptographic link between the current block and the previous one. It provides security and continuity of the chain.
- Nonce: A random number that miners change repeatedly to find a valid hash under the network’s difficulty level. This is important for the proof-of-work algorithm, since the correct nonce results in a hash that meets the required target.
As you can see, a Bitcoin block acts as a record-keeping unit. Once filled with valid transactions and successfully mined, a block is linked to the one before it. This creates an unbreakable chain of information that is extremely secure.
How Many Bitcoins are in a Block?
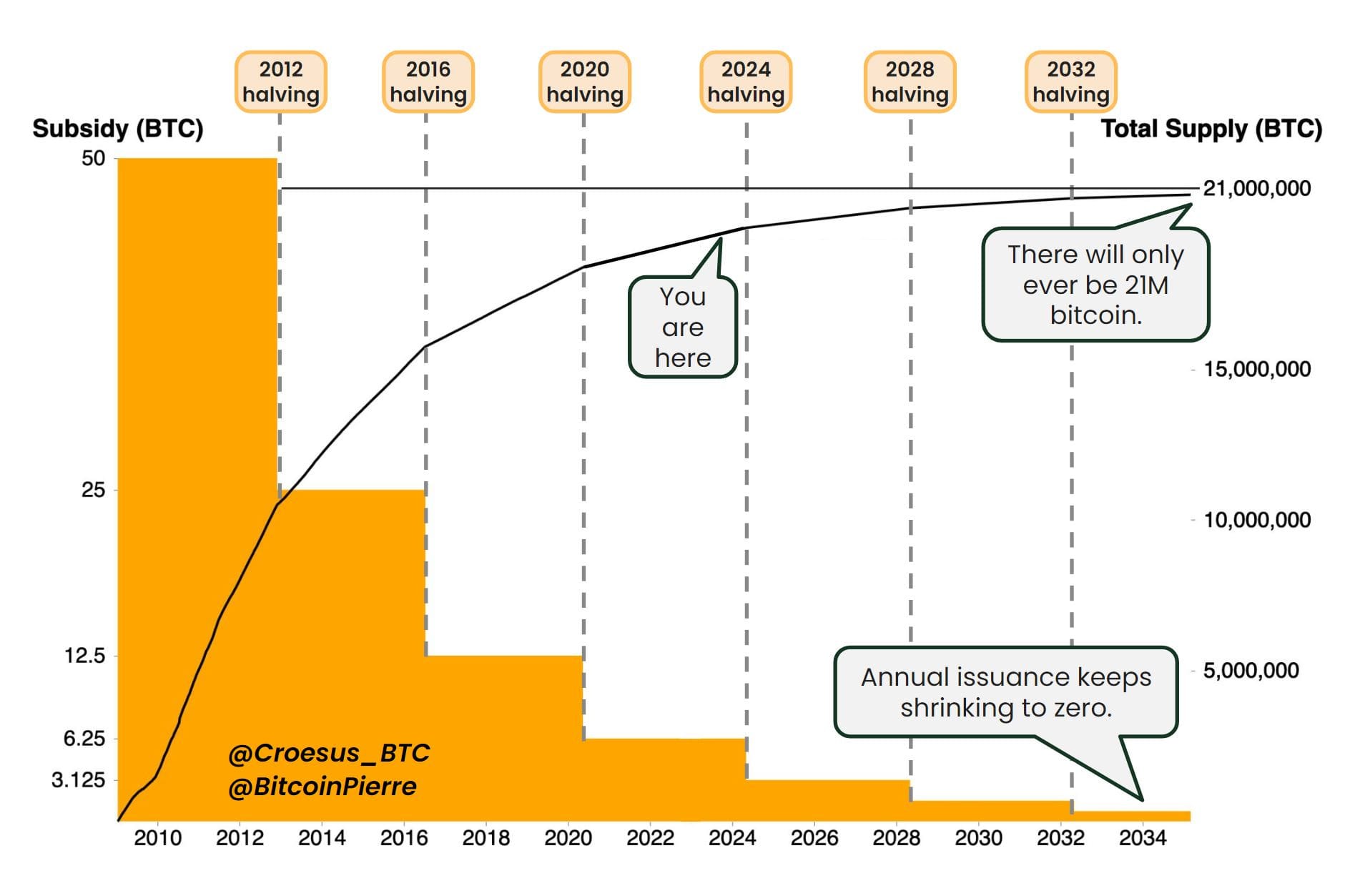
Each Bitcoin block contains a block subsidy. This is the amount of new Bitcoins awarded to the miner who successfully adds the block to the blockchain.
The current Bitcoin block reward is 3.125 BTC (July 2025)
This reward is fixed per block but is halved approximately every four years (every 210,000 blocks). This is intentional to control the supply of Bitcoin and mimic the scarcity of precious commodities like gold.
How Much is 1 Bitcoin Block Worth?
It depends on what you are using to value Bitcoin. How many steaks = 1 BTC? How many ounces of Gold = 1 BTC? How many houses = 1 BTC? How many green pieces of paper = 1 BTC?
If you are using the $ as your unit of account, then the value of a Bitcoin block depends on the market price of Bitcoin at the time the block is mined.
Here's a quick example:
- Block subsidy: 3.125 BTC
- Bitcoin price: $40,000
- Estimated block value (excluding fees): 3.125 × $40,000 = $125,000
It’s also possible to earn more from a Bitcoin block through transaction fees.
What is the Bitcoin Block Size?
The Bitcoin block size refers to the maximum amount of data that can be included in a single block.
For legacy blocks, the size is capped at 1 MB. However, with the implementation of Segregated Witness (SegWit), the effective block size can now be up to ~4 MB.
Block size impacts the Bitcoin network in two important ways:
- Transaction capacity: Considering a block can only carry 4 MB of data (~ 3,000 transactions), this is a bottleneck on base layer throughput. Only 53,000 blocks per year, meaning only 212 million transactions can be confirmed over the course of a year. Block space is a scarce resource.
- Transaction fees: Bitcoin network particpants compete for blockspace through bidding via bitcoin transaction fees, Users may pay higher fees to prioritize their transactions.
How Do You Solve/Find a Bitcoin Block?
It is more so finding a Bitcoin block than solving.
You don't need to "solve a complex math problem" you just need to find a number between 0 and 2.1 × 10^55.
Bitcoin blocks are directly tied to the mining process.
Remember the data that’s included in a Bitcoin block? This information is essential to the process of solving a Bitcoin block.
Miners are tasked with repeatedly guessing a nonce until they produce a block hash that meets the Bitcoin network’s difficulty target. This process relies heavily on hashing to try different nonce values as quickly as possible.
Because of the sheer number of possible combinations, mining demands massive computational power, typically provided by specialized hardware called ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners.
What Happens When a Block is Added?
When a new Bitcoin block is successfully mined and added to the blockchain, a few things happen:
- Transactions Are Confirmed: All the transactions inside the new block are officially verified and recorded. They are considered final and irreversible after 6 blocks.
- The Blockchain Grows: The new block is linked to the previous one through its hash. This extends the chain and maintains the chronological order of all Bitcoin transactions.
- Consensus Is Updated: Miners across the Bitcoin network update their copies of the blockchain.
- Miner Receives a Reward: The miner who solved the block receives the Bitcoin block subsidy plus any accumulated transaction fees.
This process reinforces the decentralized, tamper-resistant nature of Bitcoin.
How Do I Get a Bitcoin Block?
To get a Bitcoin block, you need to participate in the mining process.
An easy way to get started is by using a hosted bitcoin mining.
Simple Mining offers a straightforward, premium white-glove hosting service to simplify the process for investors.
Purchase a machine through our in-house offering our in the miner marketplace to get started. We manage all the operations as low as $0.07/kWh all-in.
Learn more about our hosting services and how you can mine your first Bitcoin block without the hassle of configuring hardware and software on your own.
