Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin is pseudonymous, not anonymous. Every transaction records on a public blockchain that anyone can view and trace.
- KYC exchanges create the main identification point. Once your address links to your identity, your entire transaction history becomes visible.
- Chain analysis firms use clustering and pattern recognition to trace funds across the network. Over 80% of transactions connect to identified entities.
- Privacy requires active effort: new addresses per transaction, address separation, and careful operational practices.
- Mined Bitcoin offers a privacy advantage. Coins arrive without prior transaction history or KYC links at origin.
The short answer is yes. Bitcoin is traceable. Every transaction since January 2009 sits on a public ledger that anyone can view. This fact surprises many first-time investors who assume cryptocurrency equals anonymity. Understanding how Bitcoin traceability works shapes better investment and operational decisions.
What "Traceable" Means in Bitcoin
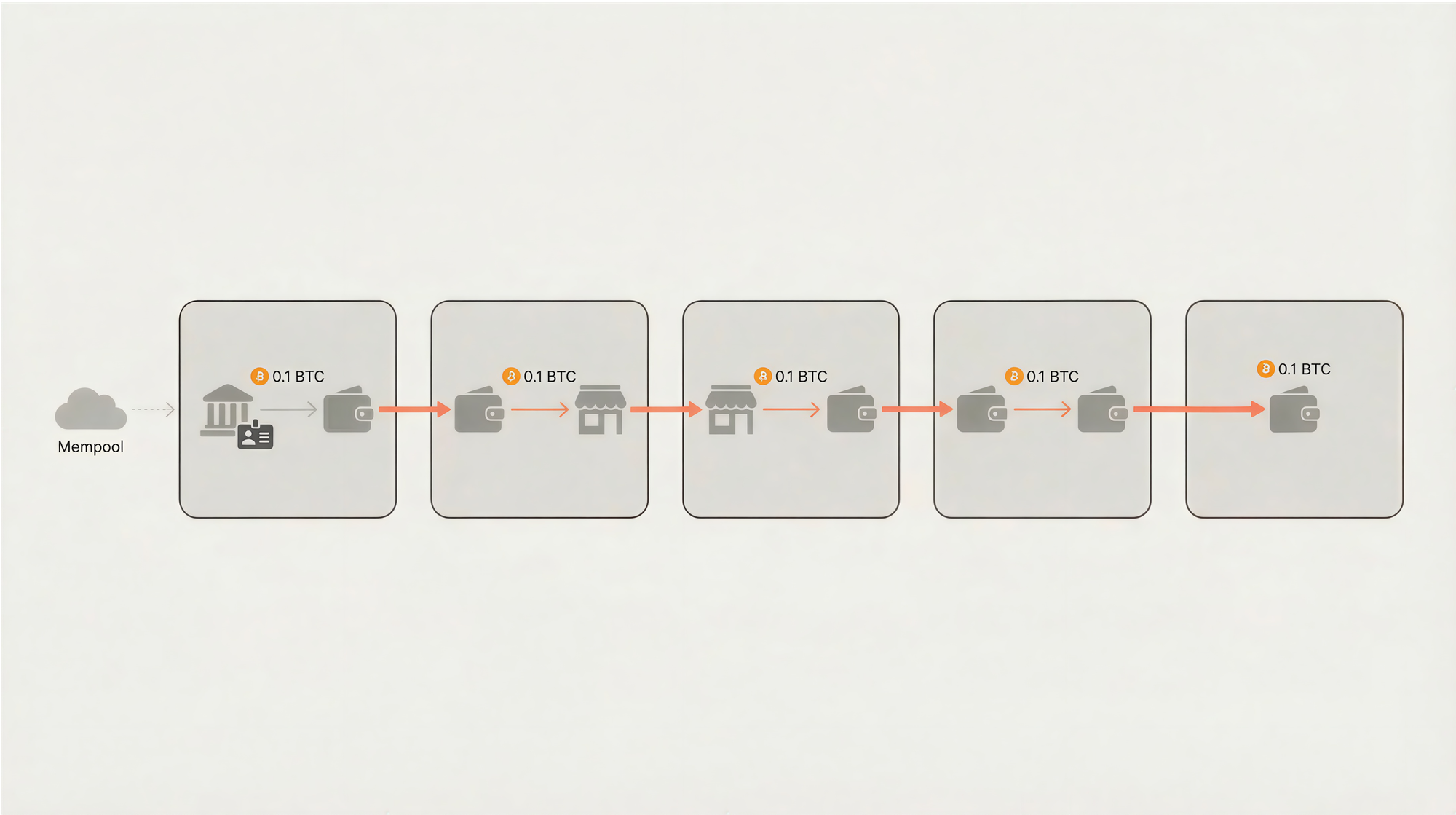
Bitcoin is pseudonymous. This term sits between anonymous and identified. Your wallet address looks like a random string of characters (1A1zP1eP...). No name attaches to it. But every movement of funds links back to that address on the blockchain.
Think of it like a public library checkout system. The card number appears on every borrowed book. Anyone can see which card borrowed what. The moment someone connects your name to that card number, your entire reading history becomes visible.
The blockchain records three things for each transaction: the sender address, the receiver address, and the amount. This data stays permanent. No one can delete or alter it. The Bitcoin protocol builds this transparency into its design as a feature for security and verification.
How Bitcoin Gets Traced
Blockchain analysis follows a clear process. Understanding each step reveals why Bitcoin privacy requires active effort.
Step 1: Transaction Broadcast. You send Bitcoin. Your transaction enters the mempool and awaits confirmation. Network nodes relay this data. Some nodes log IP addresses unless you use Tor or a VPN.
Step 2: Permanent Recording. Miners include your transaction in a block. The blockchain now holds an unchangeable record. Anyone with internet access can view it through a block explorer.
Step 3: Address Clustering. Most wallets combine multiple inputs when sending transactions. If your wallet pulls from three addresses to make one payment, analysis software infers all three belong to you. This technique links addresses across hundreds of transactions.
Step 4: Exchange Identification. Regulated exchanges require Know Your Customer (KYC) verification. You submit your ID. The exchange records which addresses belong to your account. This data does not stay internal. Exchanges share transaction records with tax authorities and blockchain forensic firms upon request. This single connection point exposes your entire transaction history for those linked addresses.
Step 5: Pattern Analysis. Firms like Chainalysis and Elliptic map billions of transactions. They tag addresses belonging to exchanges, merchants, and known entities. When your coins pass through a tagged address, the trail becomes visible.
Here is a concrete example. You buy 0.5 BTC on Coinbase. You send it to your personal wallet. That wallet address now connects to your identity through the exchange. Any funds you receive or send from that wallet can trace back to you.
Why Investors Care About Bitcoin Traceability
Traceability creates both opportunity and risk for investors. The transparent ledger supports Bitcoin's value proposition. You can verify the total supply. You can confirm transactions settled. No central authority can manipulate the records.
This same transparency raises considerations for portfolio strategy. Your holdings become visible to anyone who discovers your address. Business partners, competitors, or bad actors can track your positions. Large transactions attract attention from chain analysis firms.
What can go wrong: Address reuse creates permanent links. Posting a donation address on social media ties your public identity to all funds flowing through that wallet. One identification point cascades across your entire transaction graph.
How to mitigate: Generate new addresses for each transaction. Most modern wallets do this by default. Keep exchange holdings separate from long-term storage. Consider the privacy implications before connecting addresses to your real identity.
Decision Framework: Assessing Your Privacy Needs
Your approach to Bitcoin privacy depends on your situation. Work through these questions.
What is your threat model? A retail investor differs from a public figure. Most people face low-risk scenarios. But custody practices should match your exposure level.
Do you need fungibility? Mined Bitcoin carries no transaction history. Bitcoin purchased from exchanges links to your identity from the start. This distinction matters for some use cases.
What are your operational requirements? Business accounting demands transaction records. Personal savings benefit from address separation. Your privacy strategy should align with your goals.
If you hold significant amounts: Use hardware wallets. Generate new receiving addresses. Avoid consolidating small balances into single transactions unless necessary. Consider the chain analysis implications of each transaction.
If privacy is your priority: Explore CoinJoin implementations. Use Lightning Network for smaller transactions. Avoid KYC exchanges when possible. Accept the trade-offs in convenience.
Bitcoin Privacy vs. Privacy Coins
Some investors consider alternative cryptocurrencies for privacy. Here is an honest comparison.
Bitcoin offers transparency by design. This supports its role as sound money. Auditable supply and verifiable transactions create trust. The trade-off is reduced default privacy. Users who want privacy must take active steps.
Privacy coins like Monero obscure sender, receiver, and amount by default. This design choice optimizes for unlinkability. The trade-off is reduced auditability. Supply verification becomes harder. Regulatory scrutiny increases.
For most investors, Bitcoin remains the superior monetary asset. Its 16-year track record, network effects, and liquidity outweigh privacy limitations. The Bitcoin network processes over $10 billion in daily transaction volume. No privacy coin approaches this scale.
Active privacy practices on Bitcoin often provide sufficient protection for most use cases. The extra steps create friction. But they preserve exposure to the strongest monetary network while managing traceability concerns.
The Simple Mining Angle
Bitcoin mining offers a unique privacy advantage. Mined coins have no prior transaction history. They arrive in your wallet fresh from the block reward. No exchange database links them to your identity at origin.
Simple Mining operates 150 MW of U.S.-based infrastructure in Cedar Falls, Iowa. Our clients mine Bitcoin with a 65% renewable energy mix at $0.07-$0.08/kWh all-in rates. The mining operation delivers three benefits relevant to privacy-conscious investors.
Cleaner chain history: Your mined Bitcoin arrives without exchange tags or automated flagging history. The coins carry no prior transaction record from previous owners. You still establish a business relationship with Simple Mining as your hosting provider. But the on-chain history starts clean. No exchange withdrawal patterns. No cluster analysis linking your coins to thousands of other users. You control the privacy decisions from the first transaction forward.
Consistent accumulation: Daily mining deposits remove the timing decisions that create behavioral patterns. No lump-sum exchange purchases. No withdrawal timing to analyze.
Operational transparency: Our client dashboard provides real-time hashrate and billing data. You verify performance without trusting third parties. Precision billing charges for actual consumption.
New clients test operations with a 7-day free trial. First-year hosting includes free repairs at North America's largest ASIC repair center. The turnkey model removes operational complexity while preserving the privacy benefits of mining your own coins.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is traceable by design. This transparency secures the network and verifies supply. Investors who understand how blockchain tracking works make better custody and operational decisions. Privacy on Bitcoin requires intention. Mining provides a cleaner acquisition path than exchange purchases.
Ready to mine your own Bitcoin? Explore Simple Mining hosting options and start your 7-day free trial.
